What Are the 4 'C's of Diamond Quality ?
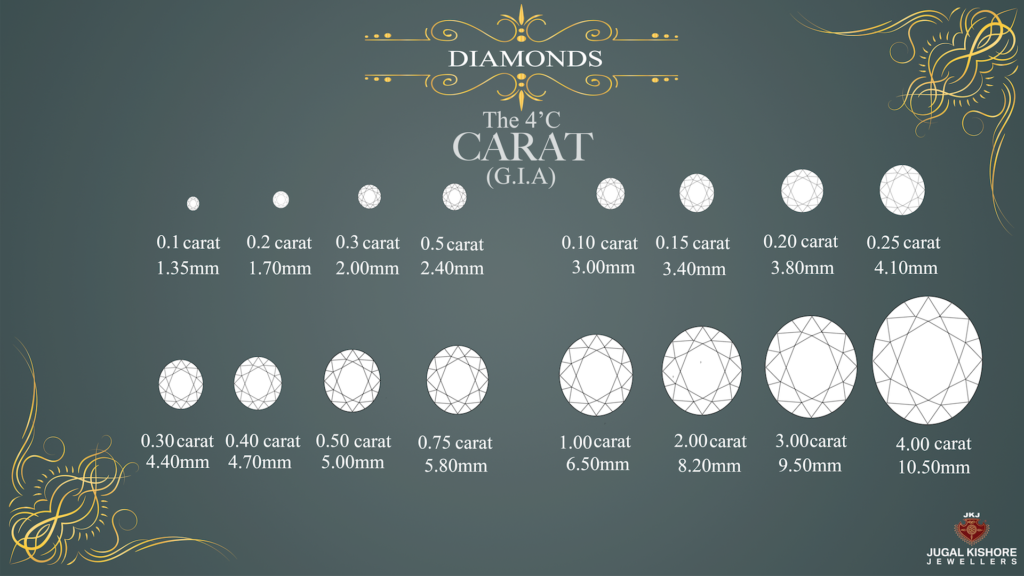
Carat
Carat refers to a diamond’s weight, not its size.Another misconception is that a bigger carat weight is in every case in a way that is better than a littler carat weight.So, the connection between carat weight and cost relies upon the extra ordinariness or accessibility of an unpleasant crystal. Be open to lowering your Carat weight to ensure you purchase a stunning diamond.
Cut
At the point when diamond gems arrive at the surface from the internal layers of the Earth, they are in their crude structure. To set them in a bit of precious stone like a necklace or ring, they should be shaped and cleaned. Diamond cut refers to the standard of a diamond’s angles, proportions, symmetrical facets, brilliance, sparkle and finishing details. These factors directly impact a diamond’s ability to sparkle, alongside its general tasteful intrigue. The GIA grades Diamond Cut on the size of Ideal, Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair and Poor. The Ideal and Excellent grades, contingent upon Diamond Shape and points cut for most extreme brightness and fire.

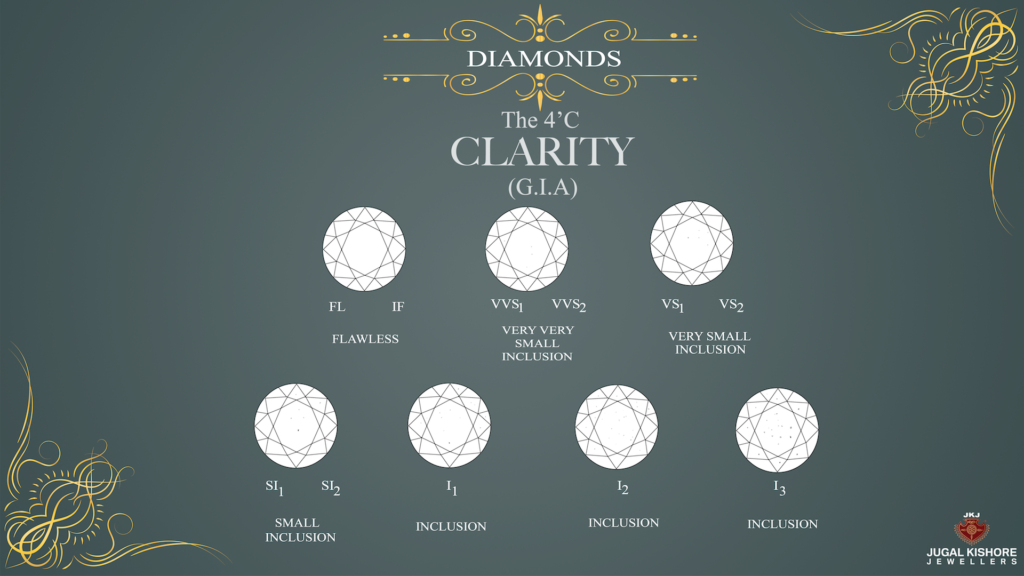
Clarity
The third most significant trademark on the rundown. Pick a diamond that is eye clean. Flaws and considerations ought not occupy from the splendor or fire of a diamond.
- FL (Flawless)
- IF (Internally Flawless)
- VVS1 (Very, Very Slightly Included 1)
- VVS2 (Very, Very Slightly Included 2)
- VS1 (Very Slightly Included 1)
- VS2 (Very Slightly Included 2)
- SI1 (Slightly Included 1)
- SI2 (Slightly Included 2)
- I1 (Inclusions 1)
- I2 (Inclusions 2)
Colour
Diamond Color is reviewed as far as how white or colorless a diamond is. For the most part, they are grouped on a GIA Color Grading System that begins with D and finishes with Z. D being the most colorless, and Z containing recognizable earthy colored or yellow color.

